Strategies V2
What is a Hummingbot Strategy?¶
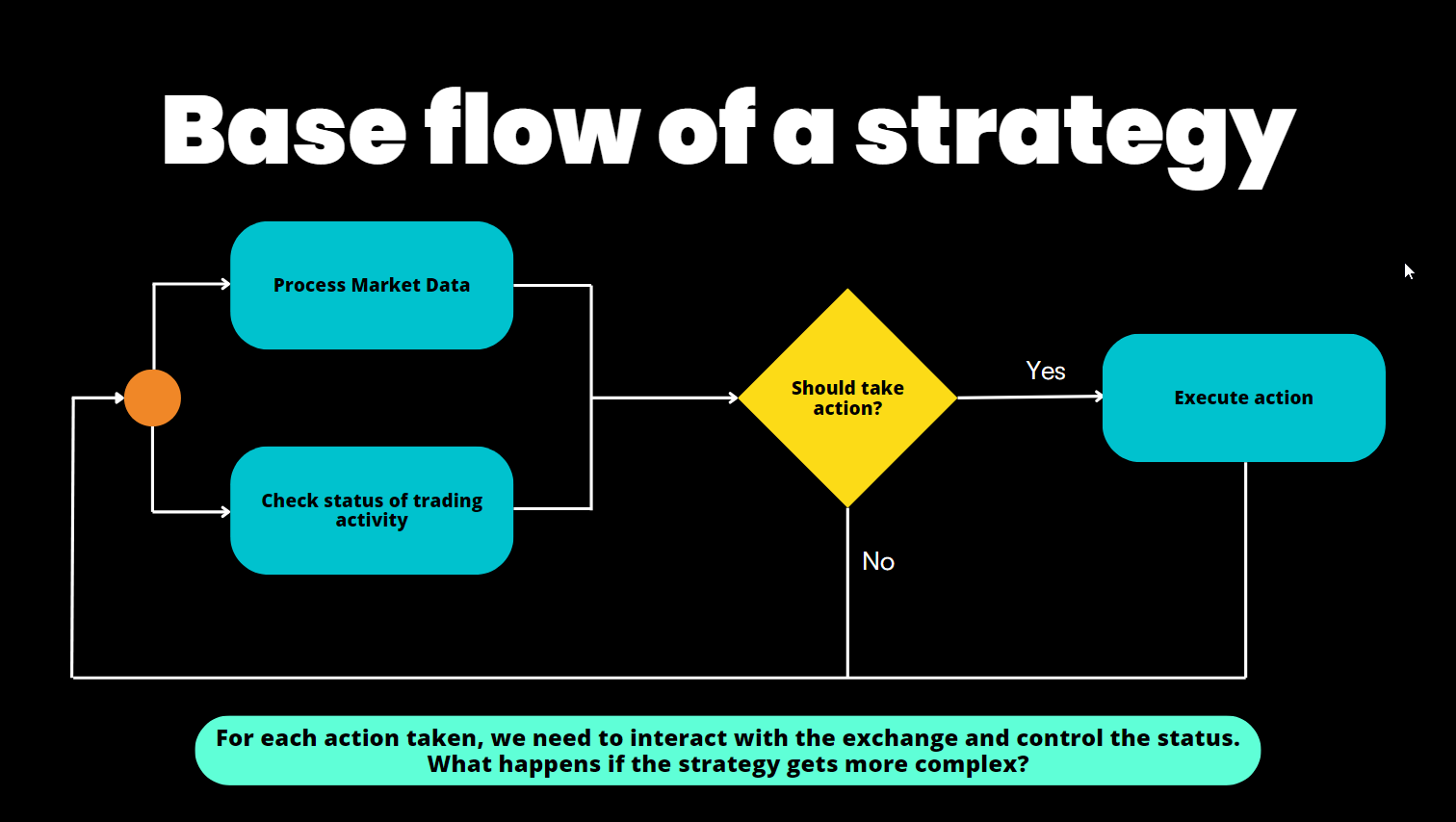
Like a computer program, an algorithmic trading strategy is a set of automated processes that executes repeatedly:
- Data Collection: Gathering real-time data from various sources
- Data Processing: Analyzing data to identify patterns and make decisions
- Order Execution: Placing and cancelling orders based on processed data
A Hummingbot strategy loads market data directly from centralized and decentralized exchanges, adaptable to the unique features of each trading venue's WebSocket/REST APIs and nodes.
Each clock tick, a strategy loads real-time order book snapshots, user balances, order status and other real-time data from trading pairs on these venues and executes the logic defined in the strategy, parametrized by a pre-defined user configuration.
To run a strategy, a user selects a strategy template, defines its input parameters in a Config File, and starts it with the start command in the Hummingbot client or via the command line with Strategy Autostart.
We encourage users to create their own custom strategies and/or extend the existing examples.
Flavors of Hummingbot Strategies¶
There are a variety of ways that Hummingbot strategies can be defined:
- Simple Scripts: A simple Python file that contains all strategy logic
- V2 Scripts: A script that uses StrategyV2 components like Candles and Executors
- V2 Controllers: Strategy logic is abstracted into a Controller, allowing a loader script to deploy and manage multiple Controller configurations
- V1 Strategies: Legacy strategy templates that not customizable
Scripts¶
Scripts are the entry point for Hummingbot strategies. They can range in complexity from a simple script that perform a single automated action to one that loads multiple Controllers. A script's on_tick method defines the actions taken each clock tick, and it provides access to core Hummingbot components like connectors.
See Sample Scripts for a full list of the current scripts in the Hummingbot codebase.
Check out this quickstart guide to learn how to code a simple market making script.
V2 Scripts¶
Scripts that use StrategyV2 components such as the Market Data Providers and Executors. Stores parameters in a script config file.
Here are the current V2 scripts in the /scripts folder:
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| v2_with_controllers.py | Generic script that loads one or more controller configurations |
| v2_directional_rsi.py | Directional strategy using the RSI indicator |
| v2_funding_rate_arb.py | Script that arbitrages funding rates across perpetual exchanges |
| v2_twap_multiple_pairs.py | Script that launches TWAPExecutors to buy/sell a block of tokens |
| v2_xemm.py | Script that launches XEMMExecutors to implement a cross-exchange market making strategy |
For more info, see Walkthrough - Script. This detailed walkthrough shows you how to use a StrategyV2 script to run a simple directional strategy.
V2 Controllers¶
Strategy logic is abstracted into a Controller. You can use the v2_with_controllers.py script to deploy one or more controller configurations, enabling you to run multiple bots more easily.
For more info, see Walkthrough - Controller, which shows you how to run a basic pure market making (PMM) strategy using a V2 Controller.
V1 Strategies¶
The original Hummingbot strategies offer structured templates for various strategies like pure market making and cross-exchange market making that let users configure parameters, but they are more rigid and less customizable than those built using the StrategyV2 framework.
See Strategies V1 for a list of these strategy templates.
Motivation for the Strategy V2 Framework¶
When it launched in 2019, Hummingbot pioneered the concept of configurable templates for algo trading strategies, such as market making strategies based on the Avellaneda & Stoikov paper.
However, the original strategy framework design had a number of limitations. Initially, strategies were confined to individual bots, complicating the management and scaling across various scenarios, and they lacked the capability to use historical market data, which forced traders to rely solely on real-time data. Furthermore, technical barriers, such as a deep prerequisite knowledge of foundational classes and Cython, hindered easy access to market data, while limited backtesting tools restricted evaluations against historical data.
In response, starting in 2023, Hummingbot Foundation began to iteratively introduce a new framework, called StrategyV2. The new framework allows you to build powerful, dynamic strategies using Lego-like components. To learn more, check out Architecture.
Learn to Develop Algo Trading Strategies
To gain a deeper understanding of how to build and deploy algo trading and market making strategies using Hummingbot's StrategyV2 framework, sign up for Botcamp, which offers courses and hands-on cohort-based professional training by the core Hummingbot maintainers.