Creating a Custom Market Making Strategy - Part 4¶
Code: https://gist.github.com/cardosofede/b1c727c3645c5ba8622496fd87838598
Video:
In this exercise, let’s extend our market making script by adding a Price Ceiling/Floor feature.
But first, let’s gain some intuition for why this feature is important for market making strategies:
Motivation¶
Markets with low liquidity are easy to manipulate, as this real-life example shows. In less than 8 hours, the price in this trading pair has pumped 39% and then returned to the original price.
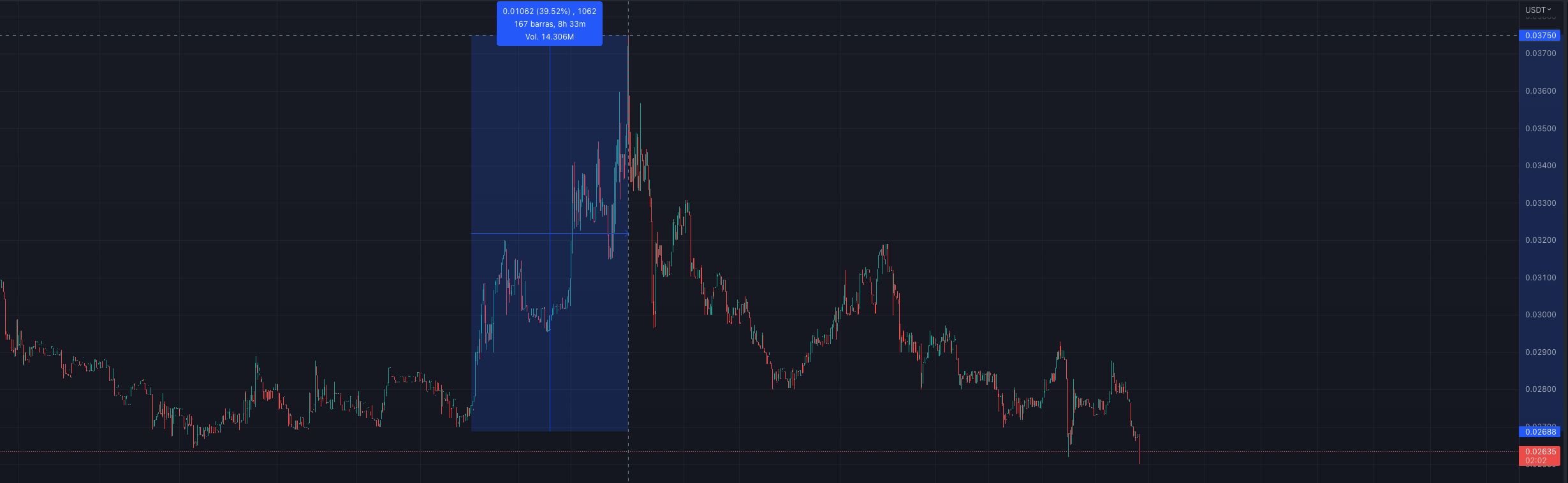
If you were a naive market maker providing liquidity all the way through this pattern, you would likely have lost money since:
- During the price uptrend, only your sell orders are executed
- After the price peaks and the downtrend starts, only your buy orders are executed
- Effectively, you sell your base asset at a lower price and buy it back at a higher price
One method to mitigate this risk is to define a price window that you will provide liquidity:
- Below a floor price, the bot won’t place
sellorders - Above a ceiling price, the bot won’t place
buyorders
So how do we define these limits?
- We can fix the floor and ceiling thresholds based on recent minimum and maximum price values.
- Let’s select the following thresholds for this example:
price_ceiling: 0.0327price_floor: 0.02736
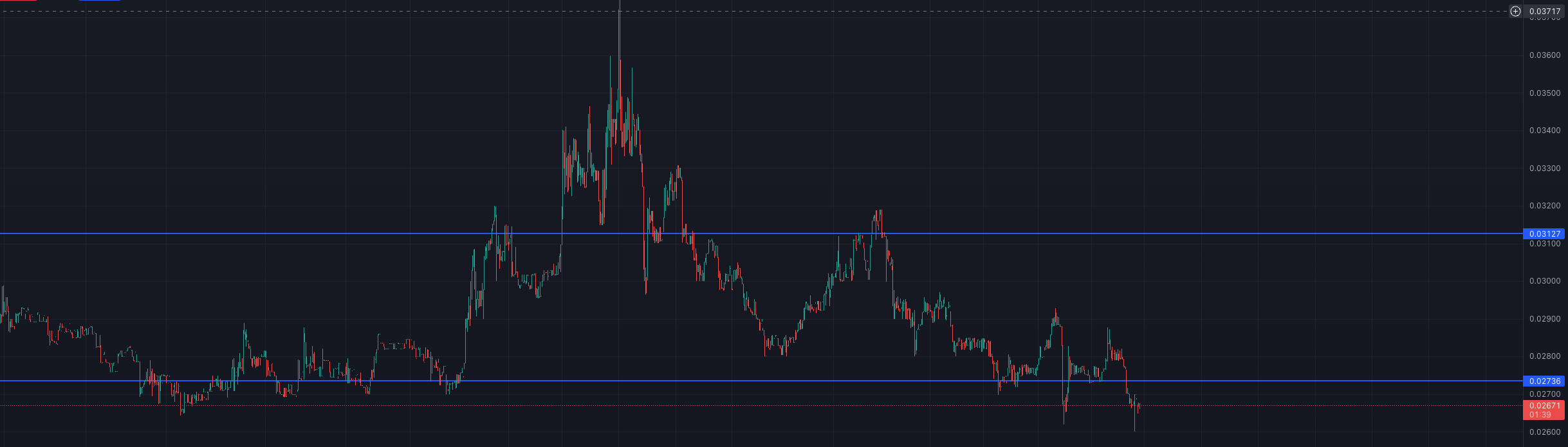
- As shown above, the bot is protected when the price goes above 0.0327 because is not going to buy more tokens. Also, if the price goes below 0.02736 the bot is not going to sell the tokens.
- In the next example, we’ll use a statistical approach to create dynamic price ceiling/floor parameters that adjust based on market conditions.
Let's code¶
We will extend the file used in the last example: quickstart_script_2.py
Let’s quickly recap the structure of the on_tick method:
def on_tick(self):
if self.create_timestamp <= self.current_timestamp:
self.cancel_all_orders()
proposal: List[OrderCandidate] = self.create_proposal()
# HERE WE CAN CHECK IF THE ORDERS ARE INSIDE THE BOUNDS
proposal_adjusted: List[OrderCandidate] = self.adjust_proposal_to_budget(proposal)
self.place_orders(proposal_adjusted)
self.create_timestamp = self.order_refresh_time + self.current_timestamp
The comment location is where we can check if the price of the sell order is above the ceiling_price or if the price of the buy order is below the floor_price.
First, let’s add these new variables to the class:
import logging
from decimal import Decimal
from typing import List
from hummingbot.core.data_type.common import OrderType, PriceType, TradeType
from hummingbot.core.data_type.order_candidate import OrderCandidate
from hummingbot.core.event.events import OrderFilledEvent
from hummingbot.strategy.script_strategy_base import ScriptStrategyBase
class QuickstartScript2(ScriptStrategyBase):
bid_spread = 0.008
ask_spread = 0.008
order_refresh_time = 15
order_amount = 0.01
create_timestamp = 0
trading_pair = "ETH-USDT"
exchange = "binance_paper_trade"
# Here you can use for example the LastTrade price to use in your strategy
price_source = PriceType.MidPrice
price_ceiling = 1700
price_floor = 1600
markets = {exchange: {trading_pair}}
Tip
Select these values based on the current market prices, as this tutorial was last updated in Feb 2023.
apply_price_ceiling_floor_filter¶
Now let’s create a method to filter the orders:
def apply_price_ceiling_floor_filter(self, proposal):
proposal_filtered = []
for order in proposal:
if order.order_side == TradeType.SELL and order.price > self.price_floor:
proposal_filtered.append(order)
elif order.order_side == TradeType.BUY and order.price < self.price_ceiling:
proposal_filtered.append(order)
return proposal_filtered
We add the new method to on_tick:
def on_tick(self):
if self.create_timestamp <= self.current_timestamp:
self.cancel_all_orders()
proposal: List[OrderCandidate] = self.create_proposal()
proposal_filtered = self.apply_price_ceiling_floor_filter(proposal)
proposal_adjusted: List[OrderCandidate] = self.adjust_proposal_to_budget(proposal_filtered)
self.place_orders(proposal_adjusted)
self.create_timestamp = self.order_refresh_time + self.current_timestamp
Running the script¶
Start and stop the script as you did before, but change the values of price ceiling/floor and using status to check the current price ceiling/floor and whether your bot is placing orders correctly.
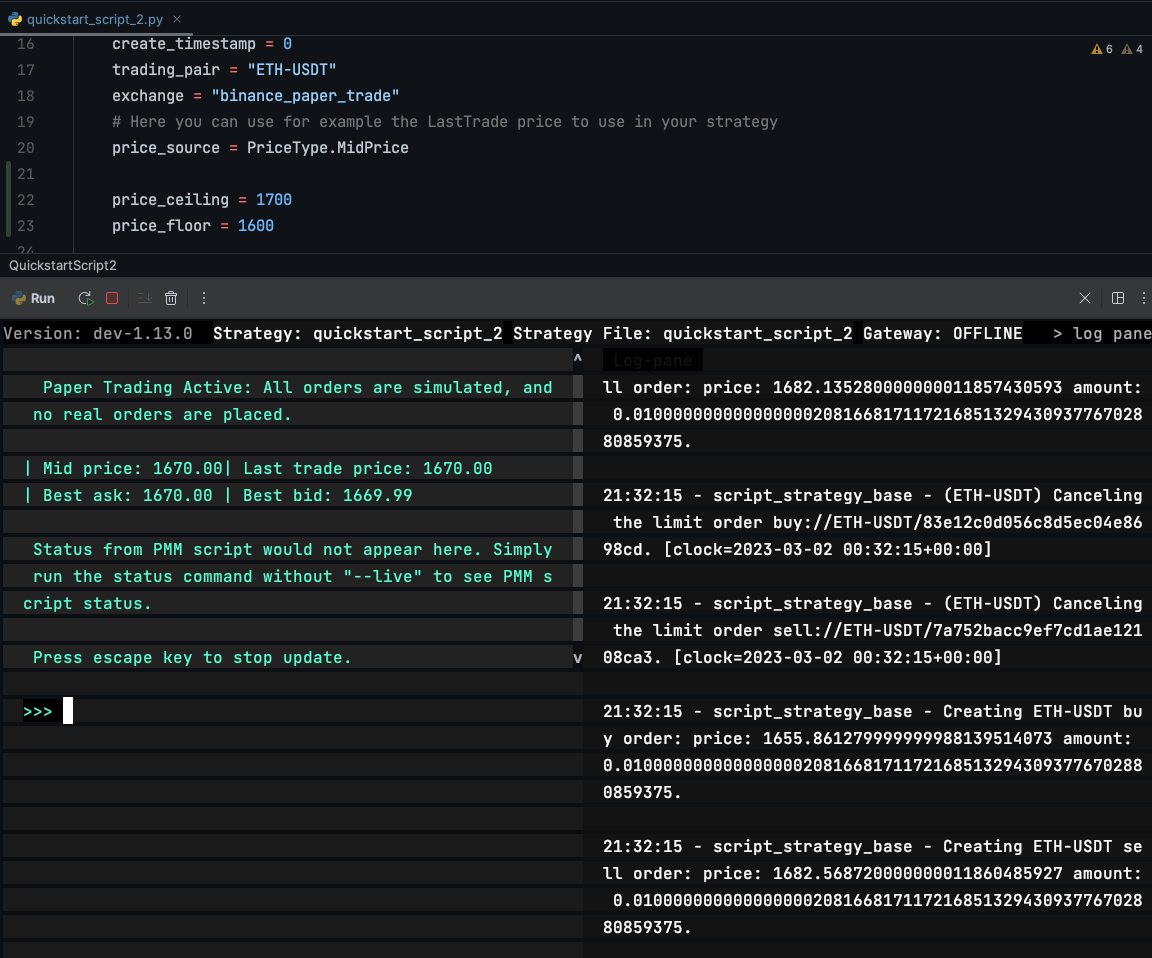
Test 1: Both orders inside range¶
- Price ceiling: 1700
- Price floor: 1600
- Current mid-price: 1670
- Sell order price: 1670 * 1.008 = 1683 (in range)
- Buy order price: 1670 * 0.992 = 1656 (in range)
The bot places both BUY and SELL orders:
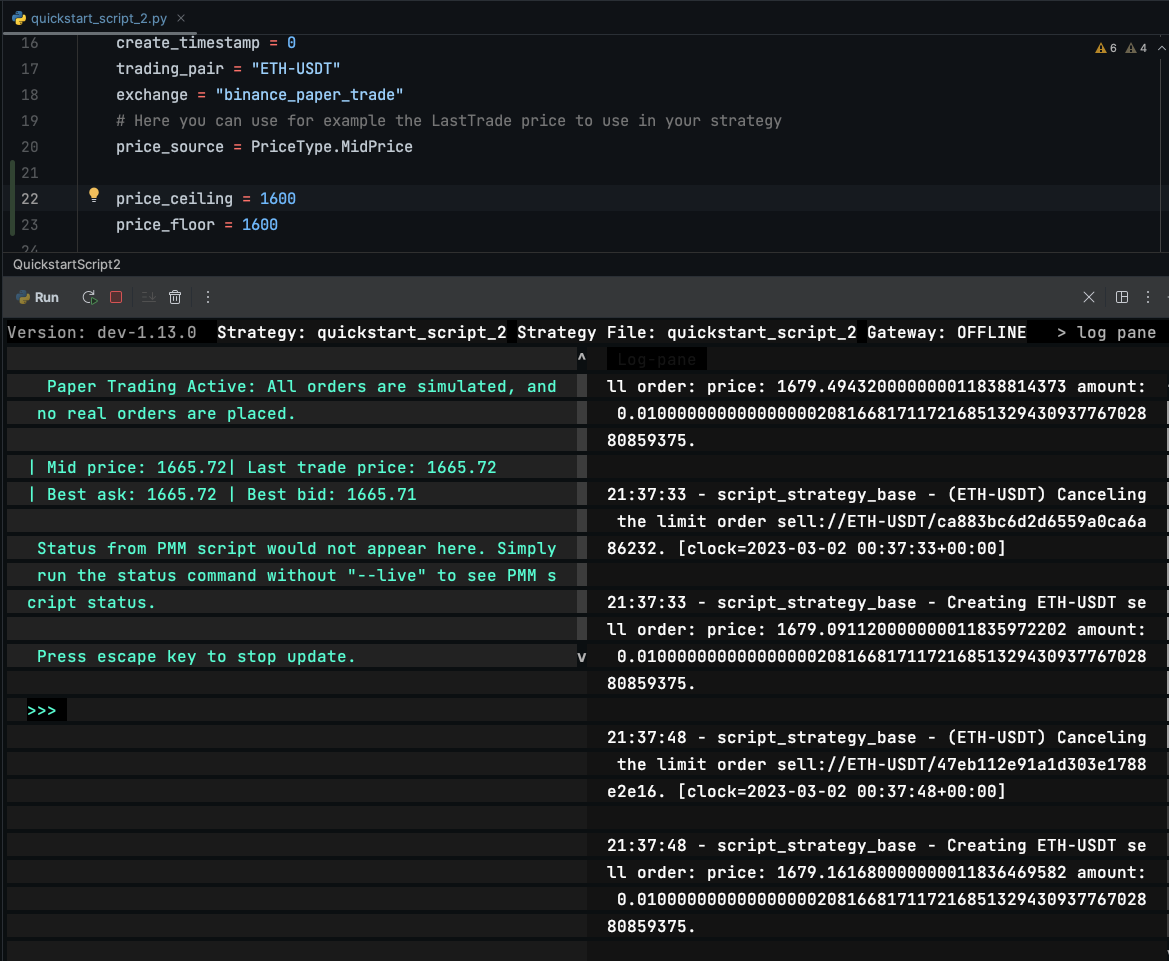
Test 2: Buy orders out of range¶
- Price floor: 1600
- Price ceiling: 1600
- Current mid-price: 1665
- Sell order price: 1665 * 1.008 = 1678 (out of range)
- Buy order price: 1665 * 0.992 = 1651 (in range)
The bot only places SELL orders:
Next steps¶
In the final part of this guide, let's make this feature more dynamic based on market data!
